Extended sources¶
This page includes some basic information on the facility that ixpeobssim
provides for the analysis of extended sources.
Warning
This section is a stub, and should be expanded to cover the classes for the simulation and analysis of extended sources.
Large-scale polarization signatures¶
ixpeobssim facilitates the search for large-scale polarization signatures
in extended sources through the xpstokesalign application,
which takes a photon list as an input and aligns the reconstructed Stokes parameters
to a given polarization model, overwriting the relevant columns.
Note
New in version 20.1.0.
The alignment of the polarization of the input events with a space-dependent
model has been recast in Stokes-parameter space, as opposed to the original
implementation that operated on the photo-electron azimuthal angles.
Accordingly, the associated tool has been renamed from xpphialign to
xpstokesalign.
xpstokesalign processes a photon list rotating the Stokes parameters so that, on an event-by-event basis, the zero for the measurement of the polarization is aligned to a given input model at the position of the event
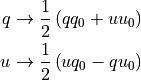
In the simplest form the alignment can be either radial or tangential, which is achieved by selecting the RAD or TAN modes, respectively, and optionally passing the right ascension and the declination of the center for the rotation via the –ra and –dec command-line switches.
Additionally, the user can feed into the application pairs of FITS images (in either the Q/U, X/Y components of the polarization vector or polarization degree/angle) in the same exact fashion of the machinery used for simulating complex polarization patterns for extended sources in ixpeobssim. This is achieved via a combination of the QU, XY of PDA modes, along with the proper model files passed to the –modelfiles command-line switch.
The supported alignment algorithms are:
RAD: radial
TAN: tangential
QU : generic polarization model (from FITS maps of U and Q)
XY : generic polarization model (from FITS maps of polarization components)
PDA: generic polarization angle model (from a single FITS map)
